Pull Your Remote Repository Contents to Your Local Repository
There are at least three situations when a pull is required:
- Your computer fails and you need to retrieve a backup of your project.
- You want to work on the project on a different computer.
- You are working with a partner or a team of programmers on the same project.
Best Practice: Collaboration in Git
WHEN WORKING ON A TEAM: Always pull the latest code from the remote repository before making any new changes to files in Eclipse. This will help reduce the number of conflicts that may need to be merged.
You can pull by using Git Bash or EGit.
Pull Using Git Bash
To see the remote repositories currently configured in your Git, execute the following command:
git remote -v
The -v flag shows the specific URLs that Git has stored for each remote repository.
For example:
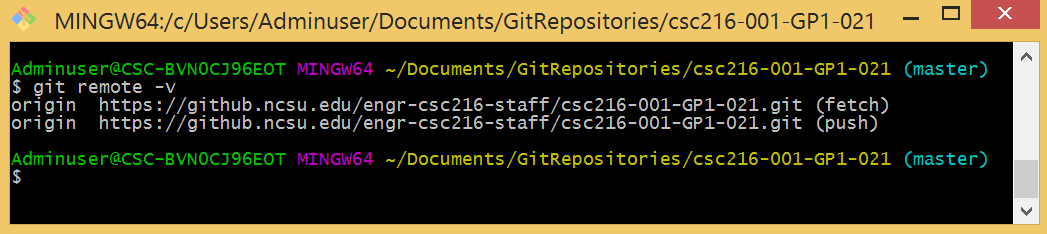
In this example, Git tells us that the “short name” for the csc216-001-GP1-021 repository URL is origin. When you clone a remote repository, the shortname defaults to origin unless you specify otherwise.
You can use the git pull command to automatically fetch and merge remote repository contents into the code in your current working directory. (The default branch name is master)
git pull [shortname] [branchname]
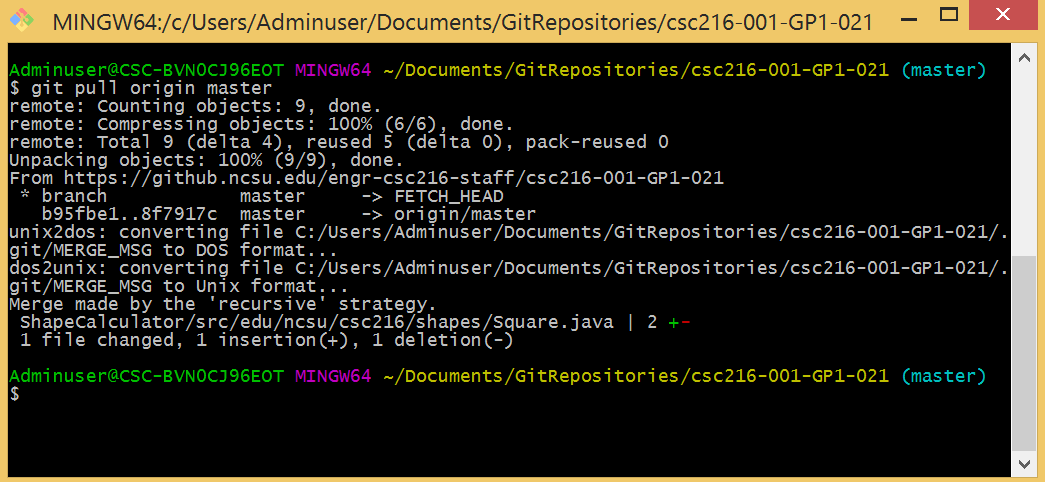
Git pulled the updated file snapshots from the remote NCSU GitHub repository.
Tool: Text Editing in Git Bash
Sometimes, you may find that Git Bash opens a text editor and waits for you to save the text file before continuing. The text editor is called Vi, and you may find it difficult to use. Please refer to online sources for more information about how to use the Vi editor. In short, to exit the Vi editor type ‘:q’ and hit the ‘enter’ key. If you want to enter a commit message, hit ‘i’ to insert. Type your commit message. The hit Esc and type ‘:wq’ to write and quit.
Alternatively, you can also change the default text editor in Git Bash. For example, in Windows, you can execute:
git config --global core.editor notepad
to use the Windows Notepad text editor instead of Vi.
Pull Using EGit
To use EGit for pulling code from the remote repository, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Package Explorer view in Eclipse.
- Right-click the project for the code and choose Team > Pull.
A summary window will open showing details of the Pull operation.
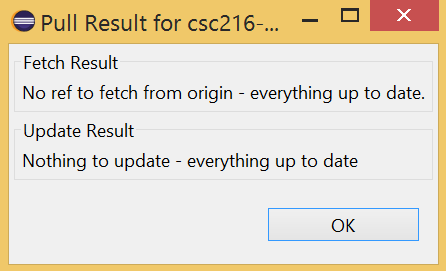
If your local repository contents match the contents of your remote repository, you will see a window similar to:
If your remote repository has updated versions of your files, you will see a window similar to the following when executing a pull request:
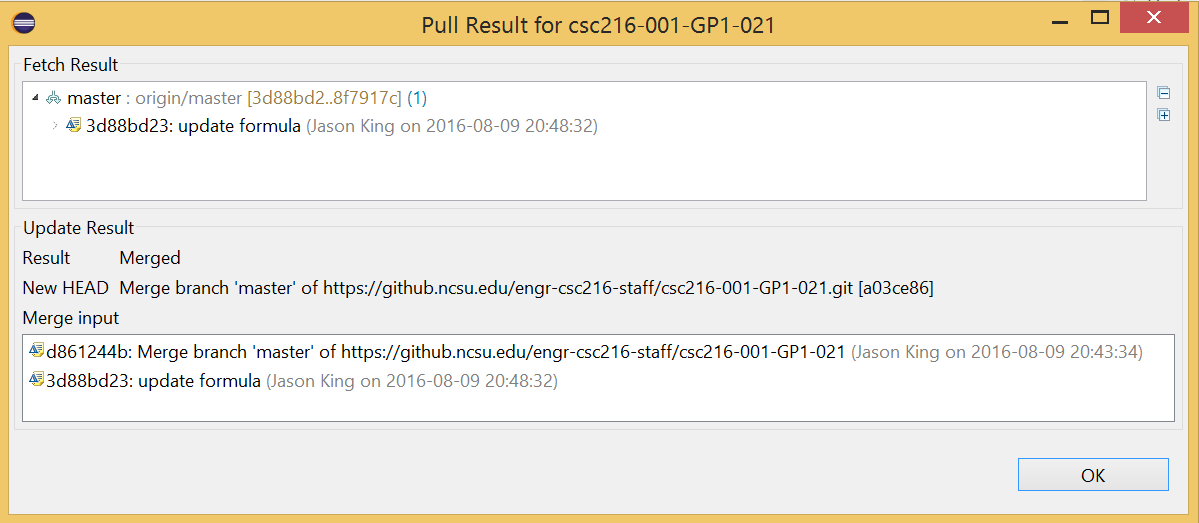
Git pulled the updated file snapshots from the remote NCSU GitHub repository.