CSC 217 Lab 11 Design
The design for Lab 11 is shown below. To follow the development paradigm of additive change, the custom LinkedListRecursive will be implemented in the edu.ncsu.csc216.pack_scheduler.util package. The FacultySchedule functionality will be added as separate classes and integrated into Faculty, RegistrationManager, Course, and CourseRecordIO.
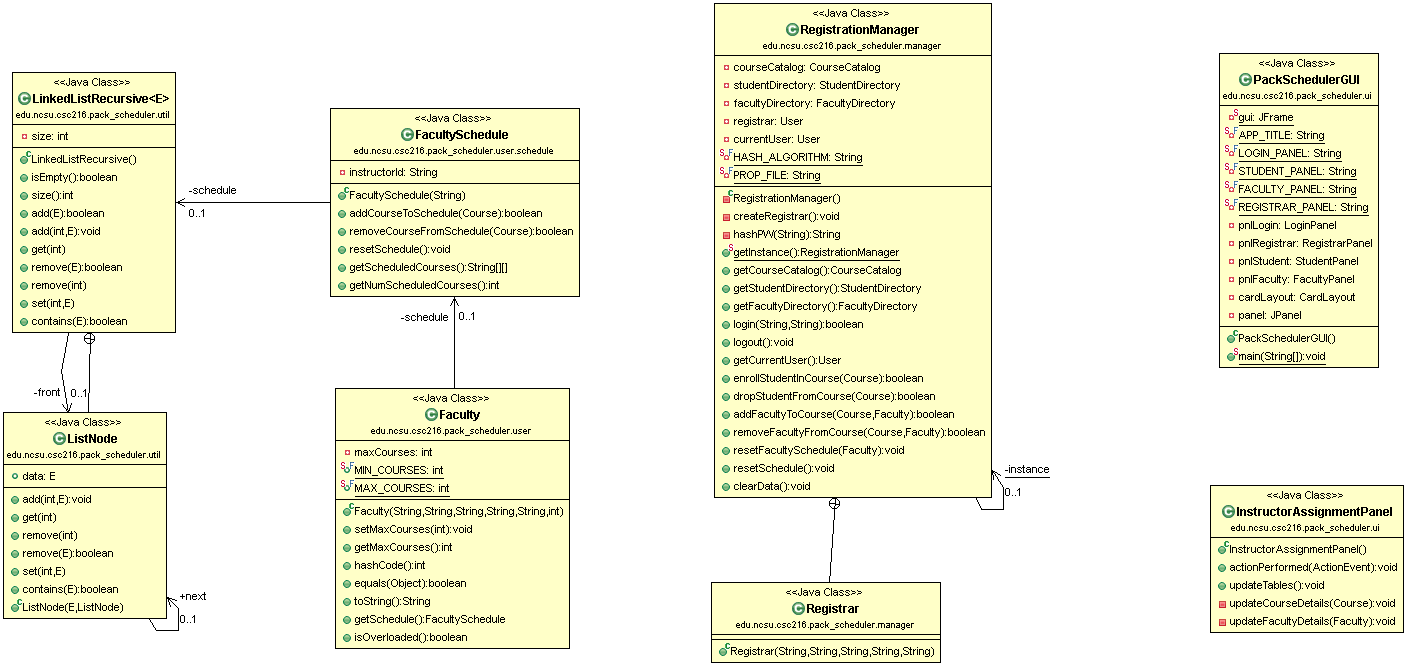
Note that Course and CourseRecordIO are not shown in the updated class diagram. While those classes will have some small changes, the design of the classes will not change!
The figure above is an example of a UML class diagram. Each class is represented by a rectangle; the text in the class describes the class members. Arrows indicate relationships between classes. The software used to generate the diagram in the figure uses the following notation conventions:
- A square (empty or solid) in front of a name means private. Solid squares are operations, empty squares are data.
- A green circle in front of a name means public. Solid circles are operations, empty circles are data.
- Members embellished with S are static.
- Members embellished with SF are static, final. (
Faculty.MAX_COURSESis public, static, and final.) - Methods embellished with C are constructors. (See
Faculty.Faculty().) - Solid arrows with simple heads indicate has-a relationships, in which one class has a member whose type is another class or interface. The containing class is at the tail of the arrow and the class that is contained is at the head. The arrow is decorated with the name and access of the member in the containing class (- for private, + for public). The arrow is also decorated with the “multiplicity” of the relationship, where 0..1 means there is 1 instance of the member in the containing class and 0..* means there are many, usually indicating a collection such as an array. (
Facultyhas a private member namedschedulethat is aFacultySchedule.) - The connector with a circle containing a cross indicates an inner class relationship. The class with the crossed circle is the enclosing class and the other class is the inner class.
The following sections will provide details about how to implement the changes to the design.